In late August, we reported about the clinical trial landscape utilizing immune cell-based therapies for COVID-19. The original search revealed 15 total relevant trials, out of which 6 were registered as Phase 1, 7 trials were Phase 1/2, and 1 trial was a Phase 2 trial (1 additional trial had no phase designation listed).
For this updated post, we revisited our search parameters to provide you with current data on the clinical trial landscape.
To obtain the results, we queried the clinicaltrials.gov database using the following search terms:
| Intervention/treatment: | “Immune Cells” OR “NK Cells” OR “Natural Killer Cells” OR “T cells” OR “T Regulatory Cells” OR “Antigen-presenting Cells” OR “CAR” |
| Condition or Diseases: | “COVID-19” |
As of October 31, 2020, the clinicaltrials.gov website had 18 “active” immune cell-based trials for COVID-19 (email us for the spreadsheet). Within the last 3 months, no trials have yet been completed, and only 1 of the new studies is US-based. See Table 1 for a brief description.
Table 1 | New Immune Cell-based Clinical Trials for COVID-19
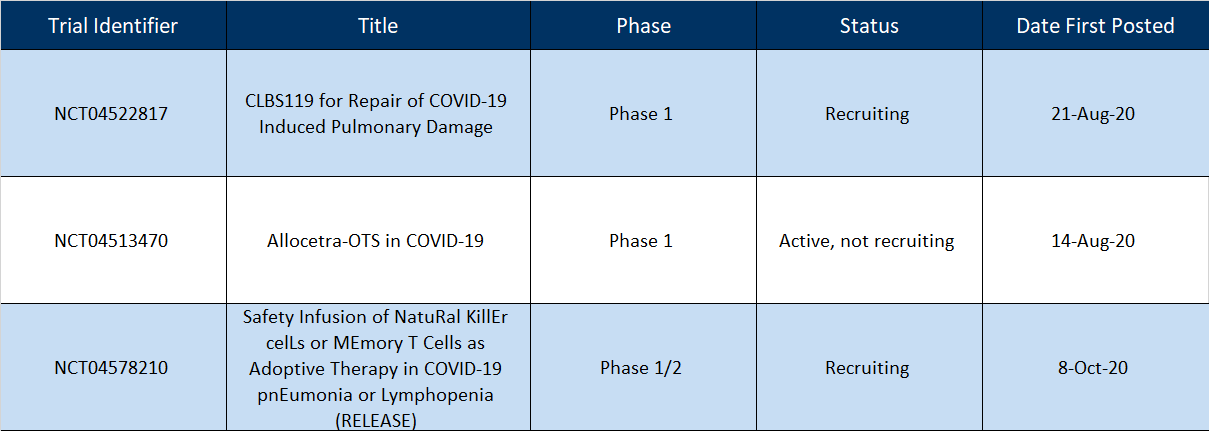
It is not surprising that of the 3 newly added trials, 1 study is evaluating autologous cells and the other 2 trials are treating patients with allogeneic cell therapies. Allogeneic cell therapies can be made in advance, can be made available as soon as the patient requires treatment, and non-responding patients could be re-infused as needed. Production failure is minimized, and at-scale manufacturing is optimized due to the “off-the-shelf” nature of the allogeneic cell product.
Although no clinical trials were completed to date, understanding the SARS-CoV-2 impact on the immune system is growing rapidly. This drives further development of immune cell-based therapies for COVID-19 clinical trials. For example, it was demonstrated that SARS-CoV-2-specific T cells can be found in peripheral blood of convalescent donors, and expansion of these cells is feasible for cell therapy.1, 2 As a result, researchers at the Cell Therapy Program at Children’s National Hospital are currently seeking approval for a Phase 1 trial using allogeneic COVID-19-specific T-cells. Other COVID-19 clinical trials to watch for include regulatory T cells infusion in COVID-19 patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome3, and invariant natural killer T cells (iNKT cells) therapy to reduce viral shedding and prevent inflammation-driven lung injury due to COVID-19.
Are you studying the use of immune cell-based therapies for COVID-19? Feel free to leave a comment below and check back next quarter for another update.
- Leung W, Soh TG, Linn YC, et al. Rapid production of clinical-grade SARS-CoV-2 specific T cells [published online ahead of print, 2020 Jul 31]. Adv Cell Gene Ther. 2020;e101. doi:10.1002/acg2.101
- Keller MD, Harris KM, Jensen-Wachspress MA, Kankate V, Lang H, Lazarski CA, Durkee-Shock JR, Lee PH, Chaudhry K, Webber K, Datar A, Terpilowski M, Reynolds EK, Stevenson E, Val S, Shancer Z, Zhang N, Ulrey R, Ekanem UO, Stanojevic M, Geiger AE, Liang H, Hoq F, Abraham AA, Hanley PJ, Cruz CRY, Ferrer K, Dropulic L, Gangler K, Burbelo PD, Jones RB, Cohen JI, Bollard CM. SARS-CoV-2 specific T-cells Are Rapidly Expanded for Therapeutic Use and Target Conserved Regions of Membrane Protein. Blood. 2020 Oct 26:blood.2020008488.
- Gladstone DE, Kim BS, Mooney K, Karaba AH, D’Alessio FR. Regulatory T Cells for Treating Patients With COVID-19 and Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: Two Case Reports. Ann Intern Med. 2020 Jul 6:L20-0681. doi: 10.7326/L20-0681. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 32628535; PMCID: PMC7370819.






